Blog
Tryptamines Around the World: Cultural and Historical Use
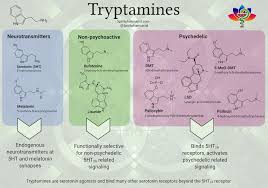
Tryptamines Around the World. Sure! Here’s an overview titled “Tryptamines Around the World: Cultural and Historical Use” — covering key tryptamines, their cultural contexts, and historical significance:
Tryptamines Around the World: Cultural and Historical Use
Introduction
Tryptamines are a class of naturally occurring compounds derived from the amino acid tryptophan. Many tryptamines have psychoactive properties and have been used by various cultures for spiritual, medicinal, and ritual purposes throughout history. This overview explores the cultural significance and historical use of some well-known tryptamines globally.
1. DMT (N,N-Dimethyltryptamine) – Tryptamines Around the World
- Source Plants: Psychotria viridis, Mimosa hostilis, Acacia species.
- Cultural Use:
DMT is a potent psychedelic found in several Amazonian plants. It is the primary active ingredient in Ayahuasca, a traditional brew used by indigenous tribes in the Amazon Basin for healing, divination, and spiritual connection. - Historical Significance:
Indigenous shamans have used ayahuasca for centuries (possibly millennia) to induce visionary states, connect with the spirit world, and treat physical and psychological ailments. - Global Influence:
Since the 20th century, ayahuasca has gained international attention for its therapeutic potential and spiritual experiences.
2. Psilocybin (4-Phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine)
- Source Organisms: Psilocybin mushrooms (e.g., Psilocybe cubensis, Psilocybe semilanceata).
- Cultural Use:
Used by indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica, including the Mazatec in Mexico, for religious ceremonies, healing rituals, and divination. - Historical Significance:
Archaeological evidence suggests use dating back thousands of years, with recorded use by the Aztecs (referred to as “teonanácatl” or “flesh of the gods”). - Modern Revival:
Interest in psilocybin has resurged for mental health treatments and research into consciousness.
3. 5-MeO-DMT (5-Methoxy-N,N-Dimethyltryptamine) – Tryptamines Around the World
- Source: Venom of the Bufo alvarius toad, and some plants.
- Cultural Use:
Used in shamanic practices by indigenous groups in South and Central America. The toad’s secretion is sometimes smoked to induce intense mystical experiences. - Historical Significance:
Less widely documented historically compared to DMT or psilocybin, but gaining prominence in modern psychedelic circles for its unique and powerful effects.
4. Ibogaine
- Source Plant: Tabernanthe iboga shrub native to Central Africa.
- Cultural Use:
Traditionally used by the Bwiti spiritual religion in Gabon and Cameroon for initiation rites and healing. - Historical Significance:
Considered a sacred sacrament, ibogaine induces deep introspective and visionary experiences and is also used in modern contexts for addiction treatment.
5. Other Notable Tryptamines
- Serotonin: Naturally occurring neurotransmitter with no known direct ritual use, but its biochemical role relates to many psychedelic tryptamines.
- Mimosa and Acacia Species: Various cultures have used these plants, often as sources of DMT, integrated into ritualistic or healing practices.
Conclusion – Tryptamines Around the World
Tryptamines have a rich and diverse history of use worldwide, often deeply intertwined with spiritual and healing traditions. Their cultural significance ranges from indigenous shamanic ceremonies to modern scientific research, reflecting humanity’s ongoing fascination with altered states of consciousness.










